Market downturns are nearly impossible to predict with any degree of accuracy. But what if there was a way to potentially capitalise even when financial markets fell?
Put options stand out in this regard. Let’s understand more about put options and how to use them. The Options Clearing Corporations also offers a helpful document that discusses the characteristics and risks of options, which can be found on their website.
What is a Put Option?
A put option is a contractual agreement that grants the holder the option to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific time period.
An important consideration here is lot size, which represents the number of shares the put option contract covers. It allows you to determine the quantity of the underlying asset you can sell if you exercise the option. Lot sizes vary depending on the specific financial instrument and exchange regulations.
The strike price is the agreed-upon price at which you can sell the underlying asset. It determines the potential profit or loss when exercising a put option. If the market price falls below the strike price, you can exercise the option and sell the asset at a higher price, effectively protecting yourself against further losses.
Investors often utilize put options as a form of hedging, which involves taking an offsetting position to protect against potential losses. This is done to minimize downside risk and create a safeguard against unfavorable market movements by purchasing put options.
It’s essential to remember that put options come with their own risks. For example, if the price of the underlying asset remains above the strike price at expiration, the put option expires worthless and the investor loses the entire premium paid for the option. Additionally, as with all options, put options are subject to time decay, meaning their value decreases as they get closer to their expiration date.
Let’s try and understand better with the help of an example.
Many companies listed on stock exchanges offer put options for their stocks. In the American options market, put options can be purchased through brokerage firms or online option trading platforms. Expiration dates for weekly options are every Friday except for the third Friday of a month. Monthly options expire on the third Friday of the month (no weekly options expire on those dates). In case of a holiday, the expiration date is adjusted to the preceding trading day.
Different Types of Put Options
How Does a Put Option Work?
When you invest in put options, your profit depends on market decline. The more the price of the underlying asset falls, the higher the profit margin.
Put option trading completion happens in two ways:
In contrast, a call option grants the holder the right to buy an asset at a predetermined price. This allows investors to make a profit if the asset increases in value.
The functioning of a put option differs from a call option in terms of rights and profit potential. Covered calls involve selling call options against an owned asset to generate income, while put options serve as a protective strategy against potential market downturns. It is important to note that buyers of the call option could lose any premiums paid for their options.
What Factors Affect the Price of a Put Option?
Several factors influence the price of a put option. These include market liquidity, sentiment, overall market conditions, and specific events or news affecting the underlying asset.
Note that these factors do not work in isolation; they influence each other and react to other market conditions to determine the final price of a put option. You must analyze these factors meticulously to make informed decisions regarding the purchase or sale of put options based on your expectations of the underlying asset’s price movement.
Making informed decisions about when and how to utilize put options is crucial. Here are some circumstances under which buying or selling put options may make sense.
When to Buy Put Options:
How to Write Put Options?
Writing put options grants the opportunity to transfer the right to sell a stock at a predetermined price to another party without imposing an obligation. This is also known as selling put options, and the option writer needs to follow these steps:
How do you exercise a put option?
To exercise a put option, notify your broker of your intention to sell the underlying asset at the predetermined strike price. Your broker will facilitate the transaction, allowing you to sell the asset.
How do you close a put option?
To close a put option position, you can either sell the put option contract before its expiration date or let it expire. You can capture any remaining value by selling the contract and exiting the position. If you let it expire, it has no value and your position is automatically closed.
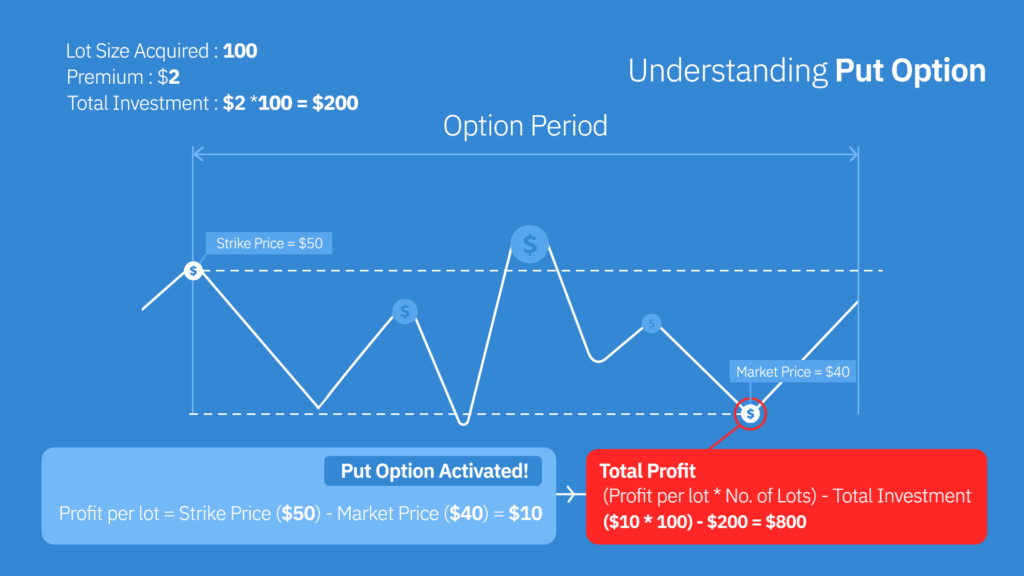
How to calculate the put option profit?
To calculate the put option profit, subtract the put option’s premium (the cost to purchase the option) from the difference between the strike price and the actual stock price at expiration. If the result is positive, it represents your profit. However, there is no profit if the result is negative or zero.
For instance, if you buy a put option for Company A with a strike price of $50 and a premium of $2, and the stock price at expiration is $40, your profit would be $8 ($50 – $40 – $2) per share. If the stock price at expiration is $60, however, there would be no profit as the option would expire without any gain.
Various trading platforms also come with an integrated options calculator to help investors.
Why is a put option called a put?
A put option is called so because it gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to ‘put’ or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined strike price within a specified timeframe. This distinguishes it from a call option, which provides the right to ‘call’ or buy the asset.
How long does a typical put options contract last?
There are various types of put options available. Some expire on the same day, whereas others expire after years. You can see the expiry date of each option before buying it.
Would you have a right or obligation if you sell a put option on a stock?
When you sell a put option, you are obligated to buy the stock at the stick price from the option buyer.
Is buying a put option similar to short selling?
Buying a put option and short selling are similar in that both option strategies aim to profit from a decline in the price of an underlying asset. The key difference is that buying a put option involves limited risk, as the maximum loss is limited to the option premium paid. In contrast, short selling has unlimited risk, as losses can theoretically exceed the initial investment.
Can you lose the entire premium paid for a put option?
Yes, it is possible to lose the entire premium paid for a put option. If the underlying asset’s price remains above the strike price at expiration, the put option expires, resulting in a loss equal to the premium paid.
Disclaimer: At the time of this article, Public does not offer options.